Convolutional Neural Networks Vs Recurrent Neural Networks(An Intuitive Guide for every Deep Learning Practitioner)
Oct 14, 2020

Have you been feeling frustared about the complexity of deep learning terms like Convolutional Neural networks and Recurrent NNs?
You have read countless articles with your goal in mind being to grasp and understand it finally - but it still doesn’t click?
Don’t worry. You’re not alone
I’ve had my fair share of frustration. Trust me, reading all those blog posts that focuses on the calculations and theory part of it and still feeling lost has led me to study it through more abstract and practical ways.
So even if you have found it difficult to assimilate, I want to clear out that situation and leave you a better deep learer with full understanding of CNNs and RNNs and excited to go forth and apply them in your projects. You can make it work, I’ll show you how.
Overview
- How Deep Learning and CNNs Relate
- CNNs Vs RNNs
- How to Differentiate between their Uses
- Applying them in your Projects
I assume that you have an understanding about Deep Learning, and maybe even CNNs. You have heard or Deep learning Countless times and Convolutional Neural networks, but how do they relate? Have you ever asked yourself!. Answering that question is the key to simplifying the mystery that surrounds CNNs. Let me answer that questions in the easiest way possible.
What is Deep Learning and CNNs ( How do they relate?)
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning in artificial intelligence that has networks capable of learning unsupervised from data that is unstructured or unlabeled. Also known as deep neural learning or deep neural network. The diagram below explains Deep learning
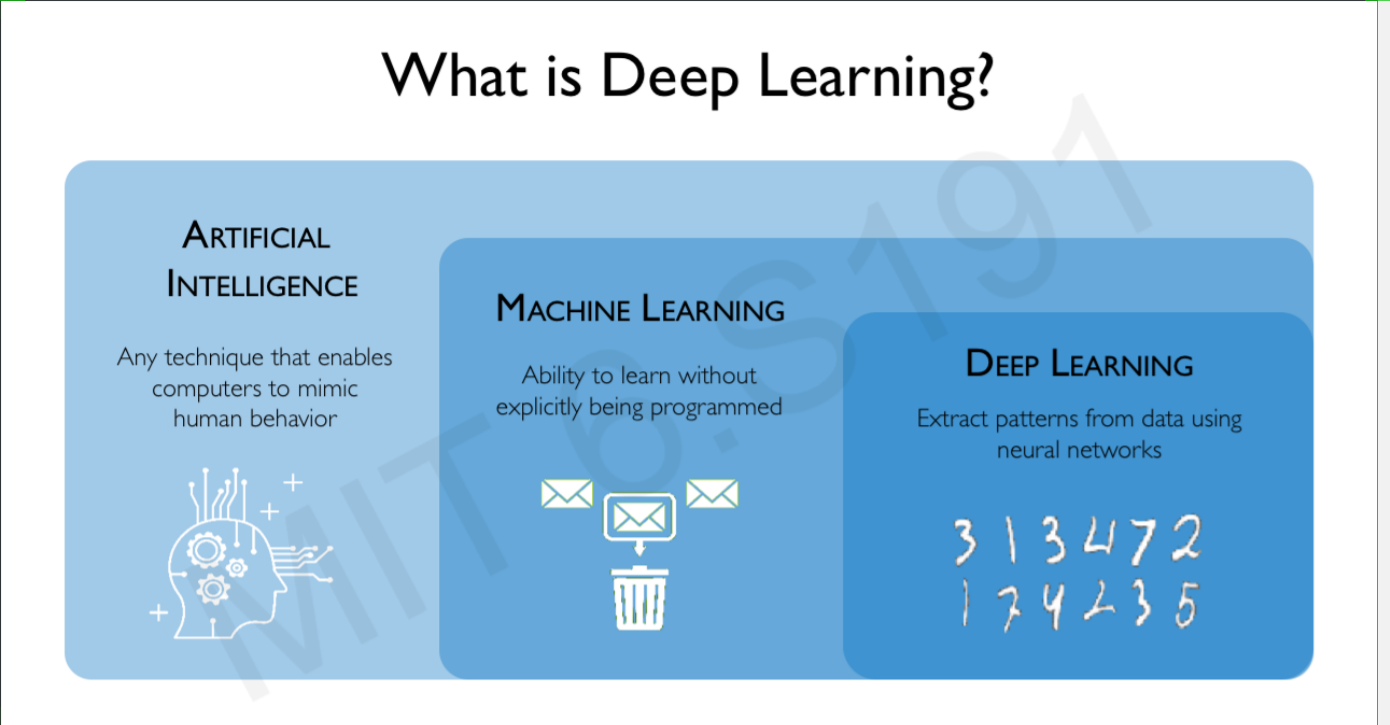
In deep learning, a Convolutional Neural Network is a class of deep neural networks, most commonly applied to analyzing visual imagery. A Convolutional Neural Network (ConvNet/CNN) is a Deep Learning algorithm which can take in an input image, assign importance (learnable weights and biases) to various aspects/objects in the image and be able to differentiate one from the other.
Recurrent Neural Networks is a neural network designed for analyzing streams of data by means of hidden units where the output from previous step are fed as input to the current step.
With the definitions above, you certainly have an idea of what Deep Learning and Convolutional Neural Networks are, but yet, this goes:
Simple and Detailed Explanation
Deep learning is a field of study that introduces the concept of “artificial neural networks” which works similarly to how the brain processes information and aims to recreate that in the processing of data by computers. In deep learning artificial neural networks are networks/ that are linked to eachother through out the system. they learn representations from data unsupervised i.e unlike regular traditional machine learning algorithm which requires an ,,, deep learning networks do not need the true output of the data to learn. These kind of data are unlabeled.
Convolutional Neural Network is a type of neural network that works specifically on image data to extract features that are unique in images, learns them through training/epochs and can carry out predictions on new unseen data using the representations learnt. This extraction of features work by passing a constant filter through the batch of images and applying a pooling layer onto the image which aims to highlight the features learnt. The convolution in CNNs means to convule/reduce the image to a smaller dimension and keep repeating this process.
Recurrent Neural Networks uses a sequential mode of working, in which the previous layer contains information that must be passed to the next layer in the step
How they Relate?
Deep Learning is a sub-field of Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence. It uses deep neural networks to learn from unstructured data.
Convolutional Neural netowrks(CNNs) are a class of Deep Neural networks(DNNs) that is used on “image data” to learn features through downsizing, kernel passing, and pooling.
On the other hand, a Recurrent neural Network is a class of DNNs that is usually used on text and sequential data for prediction the sequence of next few occurence. Examples of cases a RNN would be used: Chat/Text keyboards, Language Translation, Music Generation, etc. Now that you understand the overall concept of this subject, lets look at CNNs and RNNs on a deeper but straight forward level
CNN Vs RNN
CNNs are used to extract features from unlabeled image data. If you are working on an image data of any sort, use CNN. CNNs are used to build models that cn take as input an image and output its class(Image Classification), Objects-in-image(Object detection) and even as far as thier positions in the image(Object Localization)
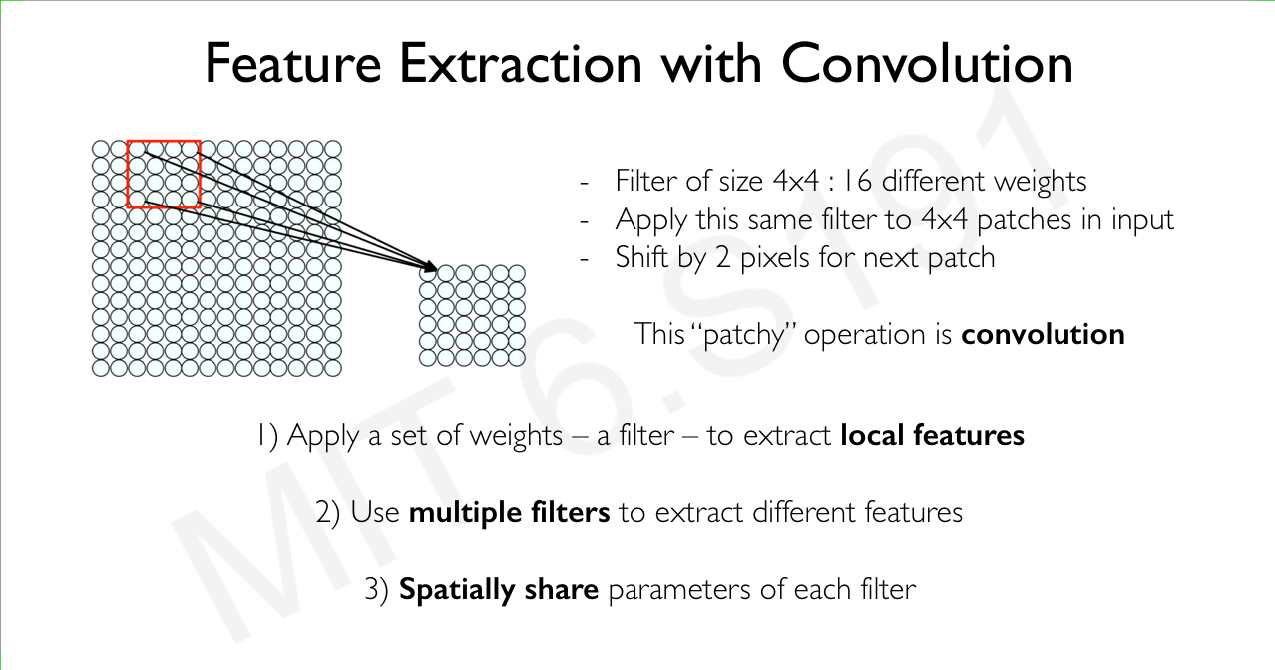
The structure of a CNN is basically a collection of neural networks, but what makes it different and unique to feature extraction in images is it’s layers and thier functions. The CNN is made up of 2 important layers; Convolution and Max Pooling. It aslo has a kernel/filter which is for sliding through the image. So here is how it works:
Example An Image of dimension 26X26 is first read and converted to 1s and 0s. Usually most images contains 3 channels which makes it a “color” image. Grayscale Images has just 1 channel. A 3X3 kernel is slided through the image. It slides through with a stride that must be defined first. The stride determines how many columns is jumped over during the sliding. So if the STRIDE = 2, it moves over 2 columns and lands on the third one. The kernel contains all the numbers in the image enclosed as fits inside the filter. This extracted number is later applied to Activation RELU where all numbers less that 1 are rounded down to 0 and numbers greater than 1 are left as they are. This activation is processed on all the extracted kernels. The last stage is usually the Max pooling layer. The Max Pool layer looks at the box of number and simply picks the highest number in the group. This is done to all the other kernels and results in new sets of numbers with one from the previous kernel box. Now that the filter has been passed through, the Max Pool reveals the strongest lines in the image which can be noticed from the pattern in its numbers. The diagram below describe the Convolution process graphically:
This explanation of CNNs shou;d give you a basic understanding of it’s concept and workings, however for you to deeply “see” how it works, you must practice using it. That’s a mistake I see most beginners make; you want to understand CNNs, you’ve read articles on it but really never practically worked on it. The most basic project to start off with using CNN is Image Classification. This project tutorial would guide you through How to Build an Image Classification Model and Web App with Tensorflow
RNN captures the sequential information present in the input data i.e. dependency between the words in the text while making predictions

Sequential types of data require a different typr of neural network from CNN in order to be processed. Examples of sequential data are ; audio sound waves, single characters/words making up a text, projecting the movement of stock prices, genomic sequences and many other cases.
Example This example below would explain what sequence/RNNs are, why they are used instead of CNN and in what kind of cases:

You are given a sentence: This morning I took my cat for a walk. You want to build a deep Learning network to solve the task, but theres one underlying issue, “A feed-forward DNN can only take a fixed length input vector”, and our problem here has a varying input length. Some sentence in the dataset are five words, others six and so on. Our ideal model needs to be able to handle variable lengths of inputs. There are three ways/ideas we can decide to take to solve this problem:
Idea 1
Hard code a certain length of input when defining the model hyper-pararmeters, i.e given a word: I know how to speak French | fluently. If we choose a lenght of 3 for our model then, the sentence would be trimmed to; to speak french. Using this method, we have an history problem:
Problem 1Can’t Model Long-Term Dependencies: In this problem, we need information from earler in the sentence but since our model is only using the 3 previous words, it cannot solve tasks like this.An example of a sentence with long-term dependencies: France is where I grew up, but now I live in Boston. I speak fluent __ (French)
Idea 2
Use Entire sequence as sets of counts(also called bag of words). This means that a sentence would be represented by how much each words in it appears.
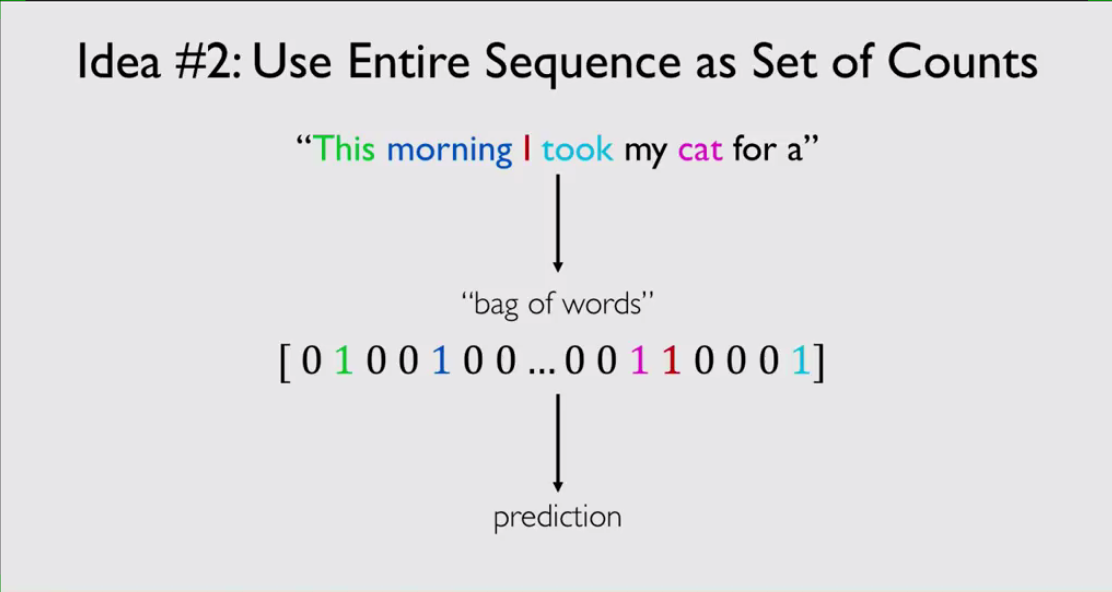
In this solution, we have a fixed length of vector which is all the possible words, and then we map a particular word to its representation in the “bag of words”. As you might have guessed, there is also a problem with this method
Problem 2:Counts don’t preserve order. We lose the sequential information in the sentence. take these two sentences for example:
Sentence 1: The food was good, not bad at all Sentence 2: The food was bad, not good at all
Because they have the same representations, thses two sentences would mean the same thing although we both know they are opposites.
The above situations are not ideal for sequential data types and information, that is where RNNs come in. Unlike the other solutions, RNNs achieve the following criteria:
- Handle variable-legnth sequences
- Track long-term dependencies
- Main information about the order
- Share parameters across the sequence
RNNs are networks that have loops in them that allows information to persist for a long period of time
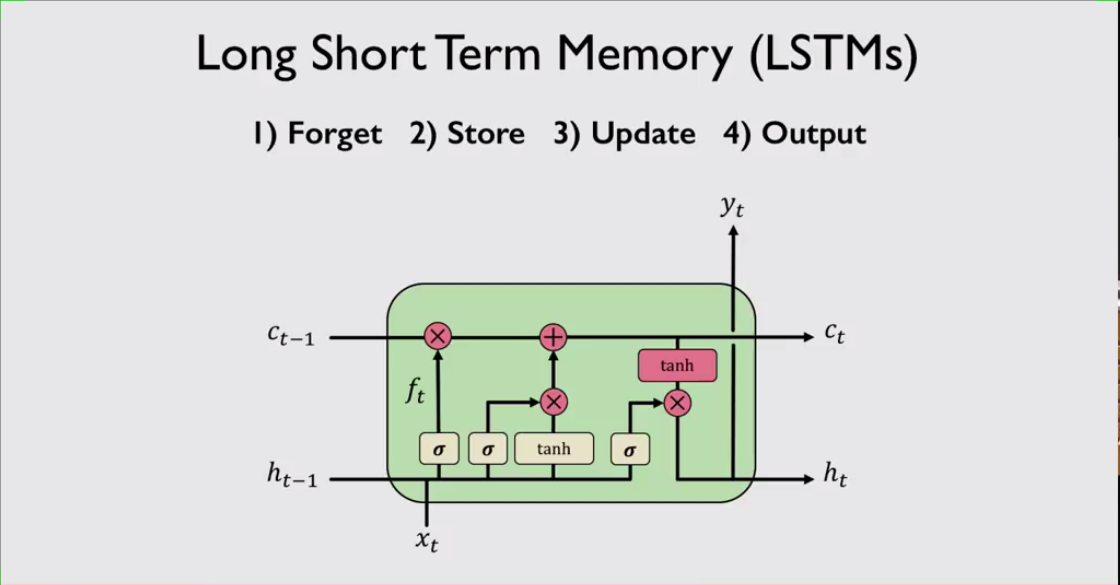
Logical example:An RNN receives and input x, propagates it through it’s network and outputs a result, while also updating it’s internal time-step which it passes this information to the next time-step. This is the process of sequential modeling, and RNNs approach to it. The RNN has three important cells which makes this process efficient and possible, they are called “gated cells”.The rnn consists of three gated cells that process how information flows from one time-step to another;
Forget: Forget gate forgets irrelevant information from the previous state
Store: Store gate stores the relevant part of new information into the cell state
Update: Update gate updates the cell using the previous and current information.
Output: Output gate controls what information it receives is sent to the next time-step
This illustration I’m sure improves your understanding about Recurrent Neural Networks. And like CNNs, it would be more profitable for you to have some practice with it to sharpen your understanding. This tensorflow article works you through in an intuitive way
Now that you know individually what CNNs and RNNs are, how they work and thier structure. Let’s look at the difference between the two. This would make it easier for you to easily indentify when to apply them
Difference Between CNNs and RNNs
| CNN | RNN |
|---|---|
| CNNs are ideal for images and video processing. | RNNs are ideal for text and speech analysis. |
| This network takes fixed size inputs and generates fixed size outputs. | RNN can handle arbitrary input/output lengths. |
| CNN is considered to be more powerful than RNN. | RNN includes less feature compatibility when compared to CNN. |
| It is suitable for spatial data such as images | RNN is suitable for temporal data, also called sequential data. |
| CNN is a type of feed-forward artificial neural network with variations of multilayer perceptrons designed to use minimal amounts of preprocessing. | RNN unlike feed forward neural networks - can use their internal memory to process arbitrary sequences of inputs. |
| CNNs use connectivity pattern between the neurons. This is inspired by the organization of the animal visual cortex, whose individual neurons are arranged in such a way that they respond to overlapping regions tilting the visual field. | Recurrent neural networks use time-series information - what a user spoke last will impact what he/she will speak next. |
These diffeences makes it very easy for you to remeber the properties and features of either CNn or RNN. You now have a broad understanding of these terms but you don’t still know how to apply them in your projects. I’ll show you how in the next section.
Practical Use of CNNs and RNNs
CNNs are use mainly for datasets and tasks involving Image manipulation. These kind of tasks include:
-
Image Classification: Classifying an image into a class or group. The ImageNet dataset can be use for Image classification
-
Object Detection: Classifying groups of objects in an Image. The Coco Dataset is used for object detection
-
Object Localization: Locating of mapping the Locations of objects in an Image. The RCNN library can be used on any dataset with Images and annotation files.
-
Style Transfer: The transferring of the style in one image to another without damaging the latter and while retaining its information.
There are a lot more applications of CNNs mainly in the field of Computer Vision and while I have just showed you some simple projects, know that all these are built at production level with more advanced systems into the Large World changing technologies we see today like Drone Navigation, and Autonomous Vehicles.
RNNs are also used in many industries today and while that holds true, it is fair to say that CNNs are more widely used. Sone applications of RNns includes:
-
Text Translation: Mapping English words in a sequence and translating each word into a different lanuguage like Spanish or French.
-
Music Generation: RNNs being superior in sequential data, gives them ability to generate chords of music after being trained on a latge collection of music data. Usually, an RNn would generate music similar to the one it has been trained on
End Notes
Now the end of this comprehensive article, I mostly hope that it has achieved it’s purpose with you; To simplify the subject of RNN and CNN without much alogrithm and theory. It’s a really long article and you might find after sometime, you would need to refer back to it for some details. that is infact highly recommended for you to grasp the main concepts effectively. Have a question or an area you need some clarity in? Please leave me a comment and I will be glad to answer it.